4.4.4 Main Takeaways on Data Validation and Verification
Course subject(s)
Module 4. Data Collection & Analysis
Why Important?
Validation and Verification is important to add credibility to your results and conclusions, to allow your results to be used in a professional environment, and to allow for academic reproducibility and transparency
Validation is proving that your outcomes are true and based on strong (scientific) evidence.
Verification is proving that your method of research has been used in the way it is supposed to be used and is suitable for your research topic.
Validity
Threats to quantitative data validity are:
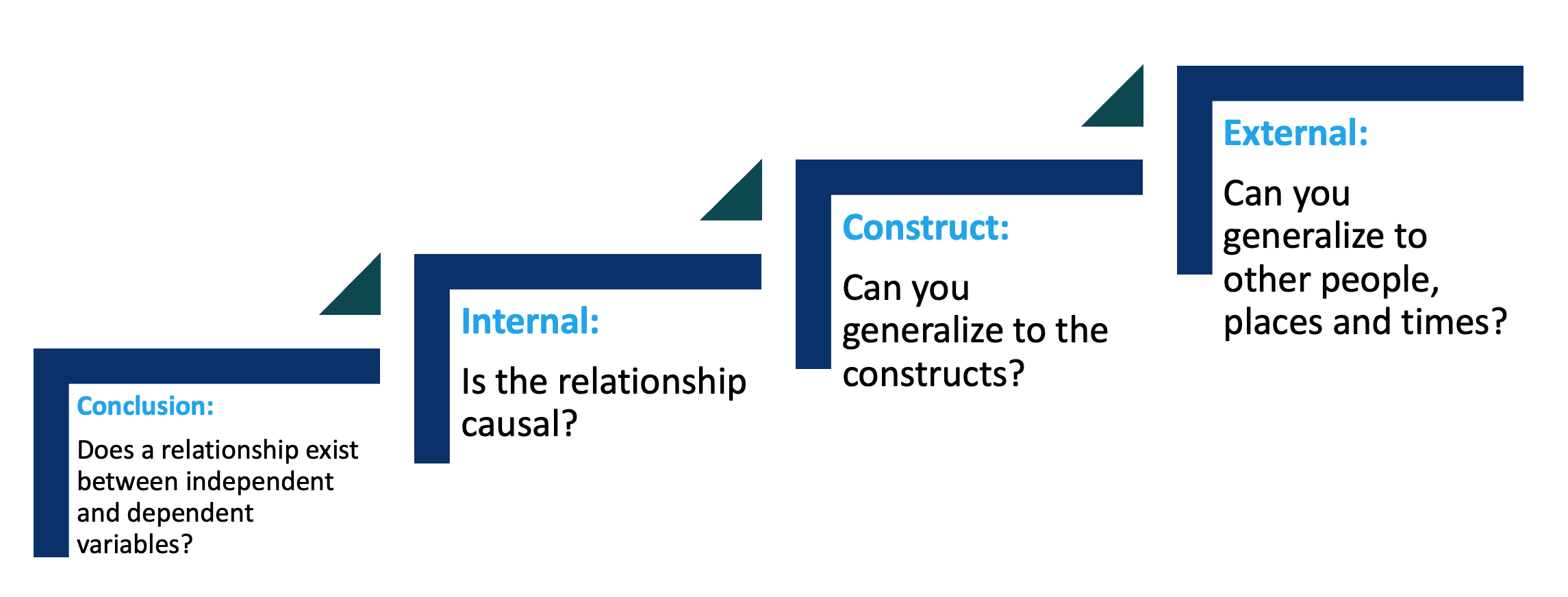
- Conclusion validity: are your (statistical) outcomes correct?
- Internal validity: have you used the correct statistical methods to establish causality?
- Construct validity: is your construct correct?
- External validity: Make sure you can actually generalize.
Threats to qualitative data conclusion validity can be reduced by reducing bias with measures such as experienced interviewers and moderators, truly representative, ethically recruited samples, triangulation methods, and respondent validation.
Verification
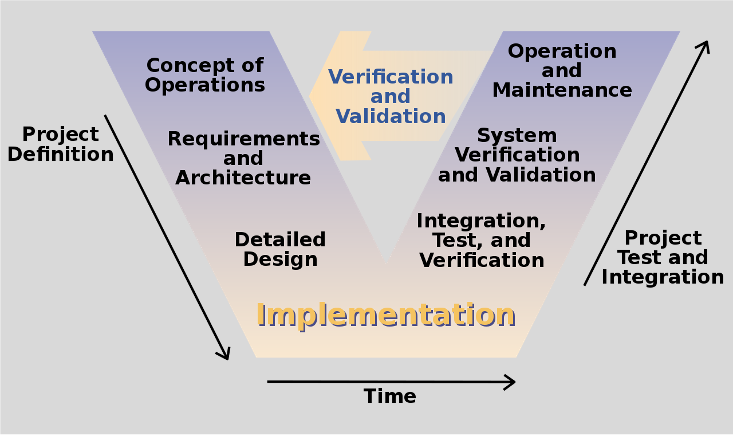
Verification of quantitative methods at the end of the process:
- For design, modeling, and systems stringent procedures in place – use V-diagram
- For statistics: verify data, measurements, procedures and compare outcomes to expectations based on research to find inconsistencies
Verification of qualitative methods takes place during the process:
- Continuous monitoring and error correction
- Focus on error prevention (see also validation)
- Monitor congruence between the research question, literature, your sample, data collection strategy, and analysis
- Strenuous record keeping
[Image: Public Domain via wikimedia.org]

Efficient HVAC Systems by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/efficient-hvac-systems//



