2.6.1 Case Study
Course subject(s)
Module 2. Addressing sustainability challenges
This section presents a case study of Urban Planning as a tool to foster more sustainable Urban Mobility. This case is in Curitiba, a city in the southern region of Brazil with a total of about 3.2 million inhabitants. It is internationally recognized as an example of practices in the use of urban planning to promote an efficient public transport system, encourage mixed land use, and create superior green public spaces.
In the late 1960s, the Structural Axes of Curitiba were conceived to improve the population’s accessibility to the public transport network. The axes were based on three parallel lanes, among which the central lane would be destined for slow traffic, concentrate commerce, and have roads dedicated to express transit lines. Also known as the “trinary” system, it has two streets parallel to the central lane dedicated for automobile circulation, in reverse directions. Some year later, an exclusive channel was installed in the central lane for the express public transportation lines.
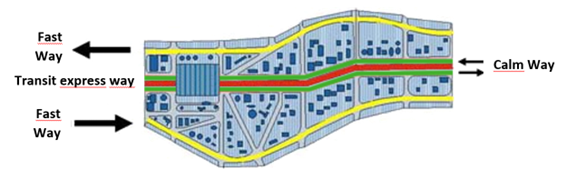
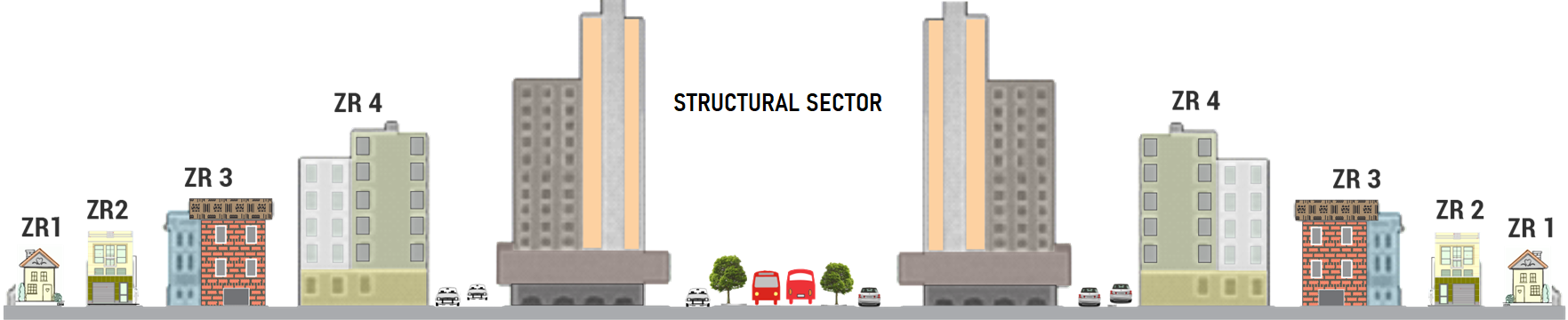
In order to stimulate occupation along these axes, zoning rules were developed to allow high construction potential in nearby areas.
 The strategies adopted have positive effects related to the dimensions of smart cities: Smart Mobility, Smart Environment, and Smart citizens, and can be adapted in other contexts to implement more efficient public transport systems, discouraging the use of individual motorized transport. In the following video, the Lecturer, Letiane Benincá presents this use case and shows how land-use planning can promote a more efficient transit system.
The strategies adopted have positive effects related to the dimensions of smart cities: Smart Mobility, Smart Environment, and Smart citizens, and can be adapted in other contexts to implement more efficient public transport systems, discouraging the use of individual motorized transport. In the following video, the Lecturer, Letiane Benincá presents this use case and shows how land-use planning can promote a more efficient transit system.
Case Study

Smart and Sustainable Cities: New Ways of Digitalization & Governance by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/smart-and-sustainable-cities-new-ways-of-digitalization-and-governance/ /



