3.2 Problem
Course subject(s)
3. Extending the model
Building a clock for a laptop

The clock speed of a computer is set in a base clock. The frequency of the base clock is multiplied in a clock multiplier, and the result is the clock speed at which the calculations are done by the CPU of the computer. We want to build a simple base clock that generates a signal of 100MHz = 108 oscillations per second. The clock multiplier that we have multiplies that frequency with a factor 16, so the CPU can run at 1.6×109 hertz = 1.6GHz.
A simple base clock is an LC-oscillator. The basis of an LC-oscillator is an electrical circuit that contains an inductor, a capacitor, a resistor and a battery.
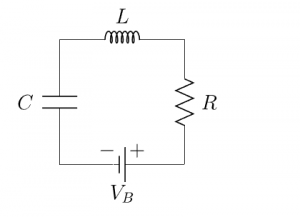
We have got a 5V battery: VB=5V, and an inductor with an induction of 0.004 microhenry: L=0.004μH. The resistance is estimated as 0.1 ohm: R=0.1Ω. We want to know what capacitor should be used.
Our problem thus becomes
Find the capacitance C of the capacitor such that the current in the electrical circuit oscillates with a frequency of 100 MHz.
Electrical engineers probably can answer this question off the top of their heads, and we admire them for that! The rest of us however needs a mathematical model, and to calculate solutions to answer this question. So, the next page is for the mathematical model for this circuit, and the calculations will hopefully be interesting for the electrical engineers as well.
On the next page, you will derive the mathematical model needed to solve the problem.

Mathematical Modeling Basics by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/mathematical-modeling-basics/.



