4.1.4 Main Takeaways Data Analysis
Course subject(s)
Module 4. Data Collection & Analysis
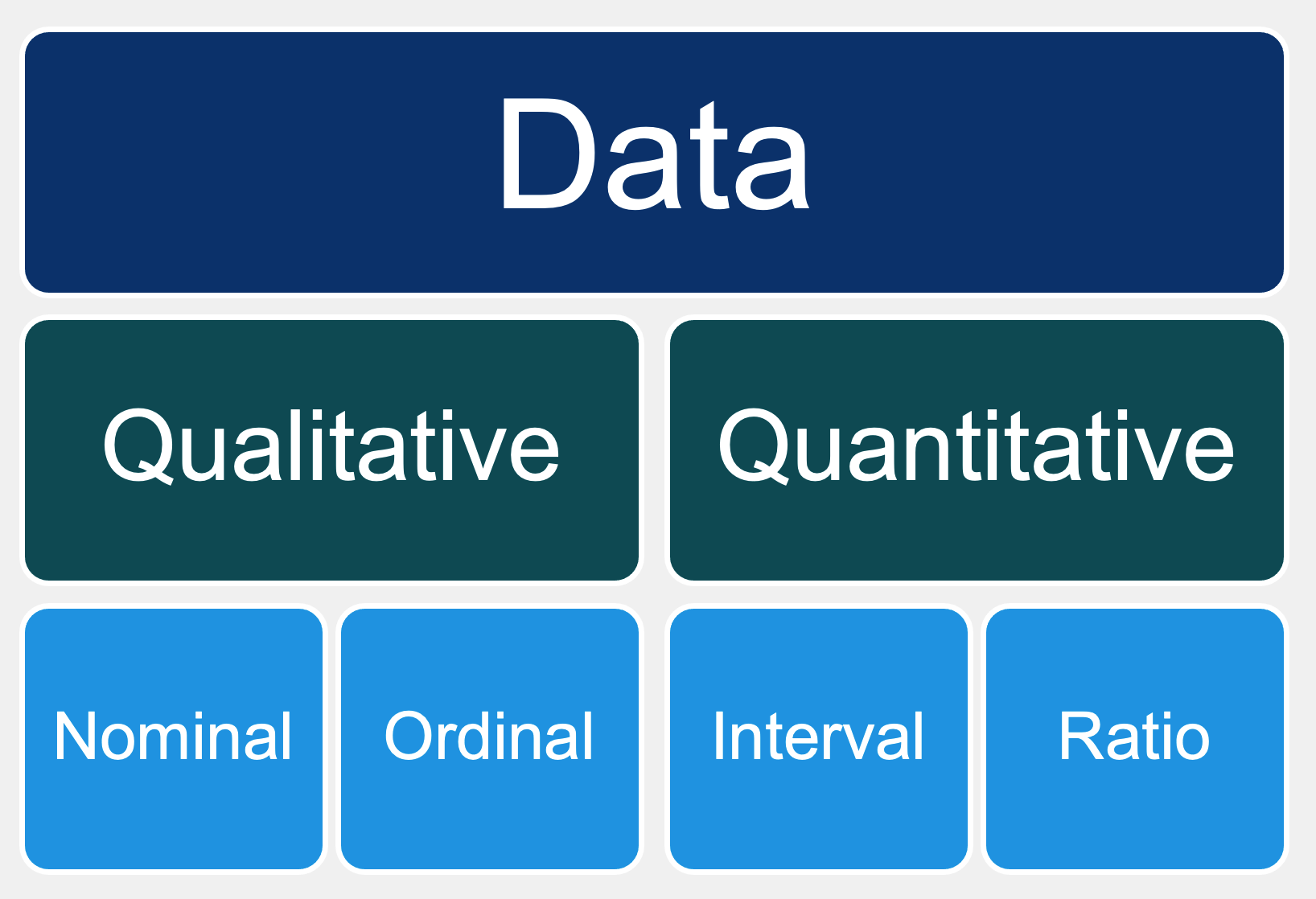 Scale
Scale
Scale: The construction of an instrument that can associate qualitative constructs with quantitative metric units
4 types of Scales exist:
Nominal – data values with no intrinsic order. It typically distinguishes groups
Ordinal – qualitative data values with some intrinsic order
Interval – numeric values on an interval scale, the order is known, exact differences in values
Ratio – as interval but with absolute zero
Data Analysis
- The purpose of data analysis is to find the answers to your research questions posed.
- It is important that you pick the right analysis tool that is Reliable and Valid for the research method you have designed and carried out.
- Every analysis tool has its pros and cons. Always carry out a trade-off on which tool is suitable for your type of data.
- Check in literature what type of data analysis can be carried out on the data you will generate
- Check if your data meets the requirements the data analysis method has,
- Run a trial with dummy data to test if the analysis tool produces correct data
- Keep track of all the data and analyses in your logbook
- If necessary create a codebook to order your data

Efficient HVAC Systems by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/efficient-hvac-systems//



