2.6.4 Main Takeaways on Validation and Verification
Course subject(s)
Module 2. Phases & Methods of Scientific Research
Validation and Verification are needed to add credibility to your results and conclusions, to allow your results to be used in a professional environment, and to allow for academic reproducibility and transparency.
Validation is proving that your outcomes are true and based on strong (scientific) evidence – Quality Assurance Process. Validity in research is the best available approximation to the truth of a given proposition, inference or conclusion.
Verification is proving that your method of research has been used in the way intended and is suitable for your research topic – Quality Control Process.
Types of Validity:
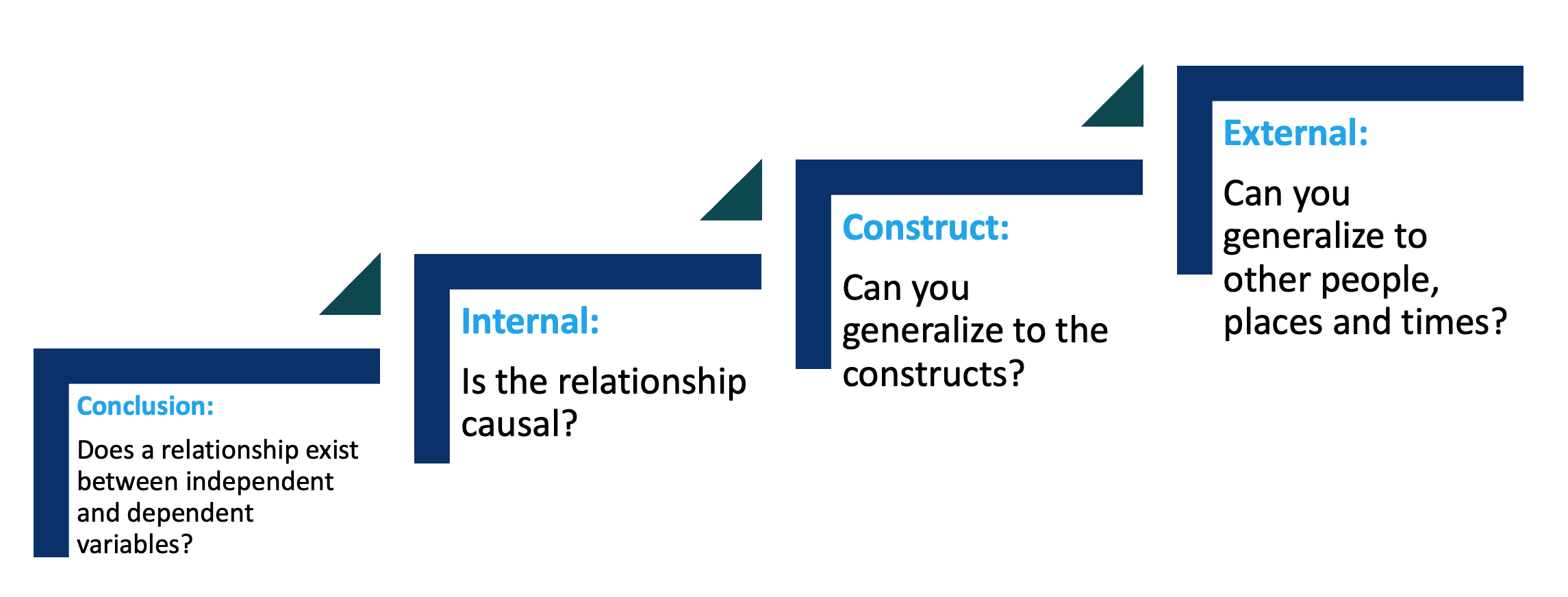
- Conclusion validity: in a research study, is there a relationship between two variables identified?
- Internal validity: if so is the relationship a causal one?
- Construct validity: given a causal relationship, did the operationalisation of the theoretical constructs reflect the ideal – typically were you able to measure what you wanted to capture?
- External validity: given the causal relation between the constructs of cause and effect, can you generalise this effect to other persons, cases, times or places etc.?

Efficient HVAC Systems by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/efficient-hvac-systems//



