2.2.6 main Takeaways on Aerospace Material Characteristics
Course subject(s)
Module 2. Materials and Manufacturing Methods
Each material has its own characteristics. Below the most important takeaways on material characteristics are highlighted.
Metals
We have seen that metals can be alloyed when liquid and that by alloying, characteristics, such as strength, can be improved. We have also seen that in aerospace, the specific properties are much more important, as weight optimization is a key design criterion.
Specific properties are properties divided by the density of the material. Under the Material Properties tab of this course, a number of material characteristics are listed.
Polymers
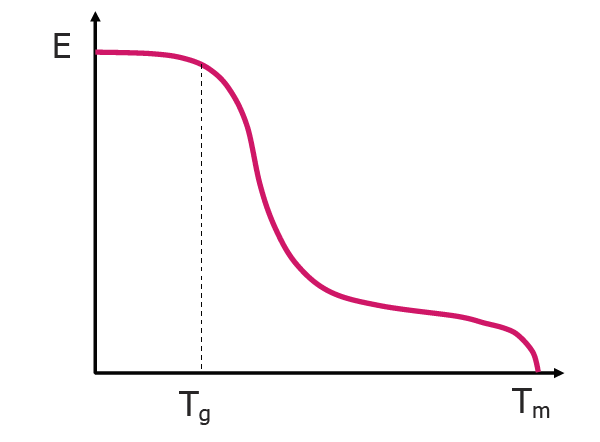
It is important to realize that thermosets are set in their ways (pun intended) and once cured cannot be manipulated in any way. Thermoplastics, however, can be heated and reformed, and will become a solid material again when cooled. When exposed to heat, a thermoset will decompose or break, whereas a thermoplastic will change “state” from a solid to a more rubbery material at the Glass Transition Temperature, 𝑇𝐺 (see also the graph displaying the declining modulus of elasticity vs. the increasing temperature) and melt when the melting temperature 𝑇𝑀 is reached.
Ceramics
Although ceramics have very good heat protection properties and can be very light, they are also very brittle and easily damaged as was illustrated by the Space Shuttle accident.
Composites
The biggest advantage of fiber-reinforced composites is that you can tailor the properties of your laminate in any way you see fit by manipulating the number of layers of fibers in a certain direction. Additionally, composites have a high specific strength and stiffness. Their downside is a low failure strain or lack of ductility.
Fiber-metal laminates make use of the best of both worlds when it comes to material characteristics and have high strength and stiffness, good ductility, good impact behavior, and good fatigue resistance.
To estimate the material properties of composites, the rule of mixtures is used to estimate the density of fiber-reinforced composites (FRP):
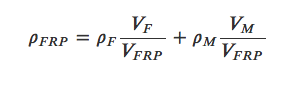

Introduction to Aerospace Structures and Materials by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://online-learning.tudelft.nl/courses/introduction-to-aerospace-structures-and-materials/.



