Smart grids explained
Course subject(s)
Module 6: ICT & infrastructures
Smart grids explained
Smart Grids will play an important role in future energy systems. Many government institutions around the world have been encouraging the use of smart grids for their potential to control and deal with global warming and energy independence scenarios. Renewables, requiring smart grids, are envisaged to become the prevailing energy source to contribute achieving energy policy goals as: sustainable development including decarbonisation, security of supply including, import dependency and fuel diversity.
But what are smart grids actually? What are the potential benefits? What are the characteristics? What are the challenges? Zofia Lukzo will explain this in the next concise web lecture.
After this web lecture you will also understand why smart grids are socio-technical systems.
Quote from the Scenarios for the Development of Smart Grids in the UK: Synthesis Report (the benefits and pitfalls of smart grids):
Although our surveys show that experts agreed on the need to make electrical delivery smarter, and that smart grids can afford various benefits – particularly cost savings, network balancing, facilitating renewables and emissions reduction – many also see smart grid solutions as unproven, underdeveloped, complex and difficult to implement. Consumer engagement and demand management were identified as benefits, but consumer resistance was also considered a risk.
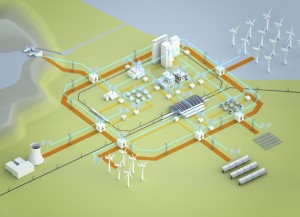
Source picture: http://www.siemens.com/press/photo/SOICSG201201-01e
Smart grid ensures that renewable energy sources can be better integrated into the grid thanks to a two-way flow of energy (orange line) and a bidirectional flow of communication data (blue green line). Whereas the generation of power in conventional power supply networks depends on consumption levels, a smart grid also is able to control consumption – depending on the availability of electrical power in the grid.
Questions for pondering
As you watch the next web lecture (and go through our suggested readings):
- What do you consider as the major challenges for realizing smart grids? Think about this from a socio-technical perspective.
- How far is your country with implementing smart grids?
- How can we use smart grids to influence demand and supply? What is needed in this respect?
- What kind of impact do smart grids have on the efficiency of traditional power plants?
- Do smart grids increase the risk of black-outs or do they do the opposite?

Next Generation Infrastructures by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at https://ocw.tudelft.nl/courses/next-generation-infrastructures/.



